Poolside pulled back the curtain just a bit more on its plans to reinvent software development using its AI platform.
In a presentation at the ai-Pulse conference, Vitor Monteiro, Head of Solutions Engineering at Poolside, outlined the company's vision to achieve artificial general intelligence (AGI) specifically for software development. He said that he Paris-based startup is taking an uncompromising approach to building what it believes will be the future of software engineering.

From Code Assistant to Digital Developer
"We're currently stuck in this code assistant lane," Monteiro explained, highlighting how current AI tools largely function as extensions that developers must repeatedly prompt for help. Poolside's vision extends far beyond this paradigm – it's working toward AI that can function as a true development colleague rather than just an assistant.
The company's roadmap envisions several evolutionary stages: from today's code assistants to junior developers, eventually progressing to senior developers, and ultimately achieving AGI for software development. This aligns with OpenAI CEO Sam Altman's vision of AI companies reaching trillion-dollar valuations – though Monteiro suggested that Poolside would be the one developing the software in such scenarios.
Technical Challenges: The Twin Bottlenecks
Poolside has identified two critical bottlenecks in achieving its goals: compute power and data. The company recently secured significant investment to build out their GPU farm, which Monteiro described not as a cause for celebration but as "a massive responsibility" to advance the field's research at scale.
The more challenging bottleneck, according to Monteiro, is data. With approximately 3 trillion tokens of source code available worldwide for training, all AI companies are essentially working with the same limited dataset. Poolside's solution? A synthetic data generation system they call "reinforcement learning from code execution feedback."
Revolutionary Approach to Training Data
The company has developed an automated system that:
- Scans open-source repositories.
- Qualifies high-quality code based on unit test coverage.
- Takes repository revisions and challenges their AI models to generate multiple solutions (up to 50 variants).
- Uses unit tests to validate solutions, creating deterministic feedback loops.
What makes this approach particularly powerful is that failed attempts become valuable training data, as the system can definitively determine what works and what doesn't through actual code execution. "Even if the model suggested something that failed all the tests, that's good data," Monteiro emphasized. This system runs continuously, generating tokens of high-quality training data that supplement existing datasets.

Enterprise-First Strategy
Poolside has prioritized enterprise solutions. The company is responding to strong demand for deployment behind corporate firewalls, allowing companies to fine-tune models on their proprietary codebases without data privacy concerns. Poolside's technology is currently available through popular IDEs including JetBrains' suite, Visual Studio Code, and Visual Studio, along with a web assistant and API access, he said.
Technical Capabilities
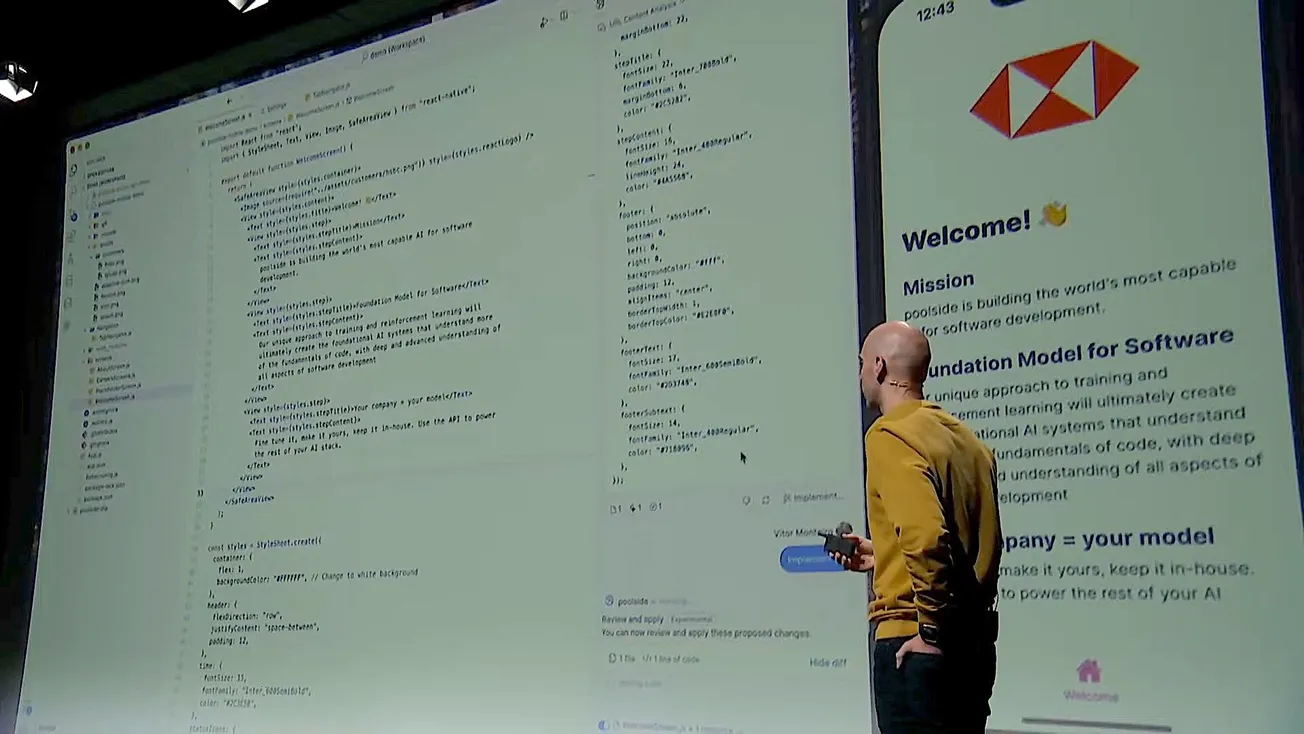
During his presentation, Monteiro demonstrated Poolside's current capabilities through a mobile app development scenario. The system showed impressive contextual understanding, handling ambiguous prompts and generating complete solutions for complex UI requirements. The demo highlighted both code completion and chat-based interaction features, with the ability to review and implement changes block by block or all at once.
With a team of approximately 20 people and their new GPU cluster secured for the next two to three years, Poolside is positioned to scale up its research and development significantly. Monteiro suggests that as their models become more capable, we'll see a shift from simple code assistance to self-sufficient agents handling various aspects of the software development lifecycle, from code reviews to project management.
Poolside's approach represents a departure from general-purpose large language models. The company firmly believes that domain-specific models are the future for specialized fields like software development, medicine, and autonomous driving. Their focus on generating synthetic training data and building purpose-built models could provide a blueprint for developing highly specialized AI systems in other fields, Monteiro said.

"Now that we have our GPU cluster in place for the next two or three years, we're pretty sure that we're going to prove the theory and the research that we did at this small scale and explode it," he said. "And maybe we can be here next year to show you where we are in that trajectory and hopefully have bridged that gap to show you an even more impressive demo."